Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Crop a raster#
This example demonstrates the cropping of a raster using geoutils.Raster.crop().
We open a raster and vector, and subset the latter.
import geoutils as gu
filename_rast = gu.examples.get_path("everest_landsat_b4")
filename_vect = gu.examples.get_path("everest_rgi_outlines")
rast = gu.Raster(filename_rast)
vect = gu.Vector(filename_vect)
vect = vect[vect["RGIId"] == "RGI60-15.10055"]
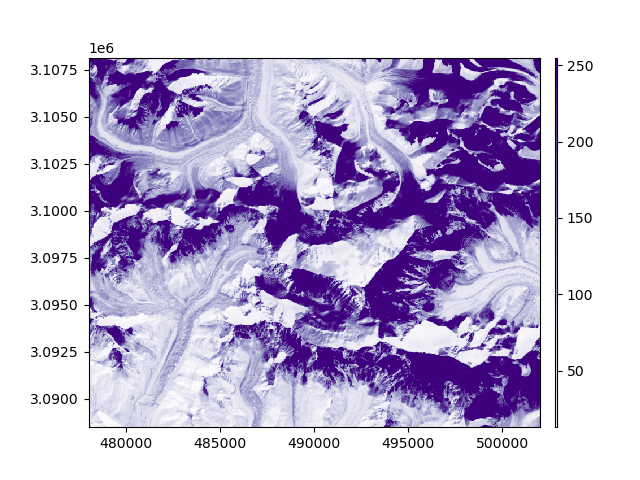
The first raster has larger extent and higher resolution than the vector.
rast.info()
print(vect.bounds)
Driver: GTiff
Opened from file: /home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/geoutils/checkouts/stable/examples/data/Everest_Landsat/LE71400412000304SGS00_B4.tif
Filename: /home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/geoutils/checkouts/stable/examples/data/Everest_Landsat/LE71400412000304SGS00_B4.tif
Loaded? False
Modified since load? False
Grid size: 800, 655
Number of bands: 1
Data types: uint8
Coordinate system: ['EPSG:32645']
Nodata value: None
Pixel interpretation: Point
Pixel size: 30.0, 30.0
Upper left corner: 478000.0, 3088490.0
Lower right corner: 502000.0, 3108140.0
BoundingBox(left=86.89820460200008, bottom=28.00781958500005, right=86.97674208800004, top=28.095011473000056)
Let’s plot the raster and vector.
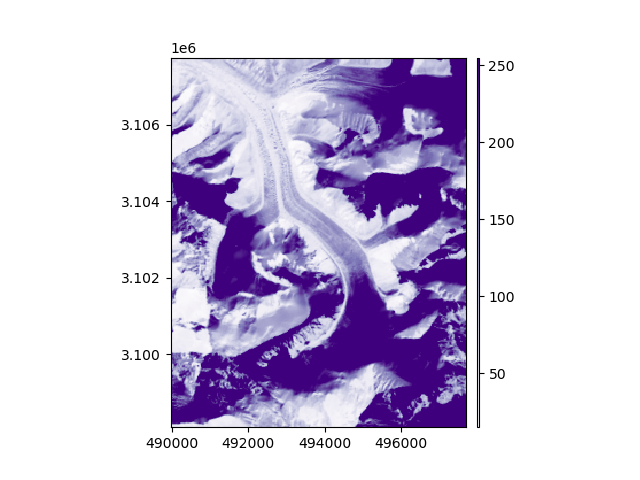
First option: using the vector as a reference to match, we reproject the raster. We simply have to pass the Vector
as single argument to crop(). See Match-reference functionality for more details.
Now the bounds should be the same as that of the vector (within the size of a pixel as the grid was not warped).
Note
By default, crop() is done in-place, replacing rast. This behaviour can be modified by passing inplace=False.
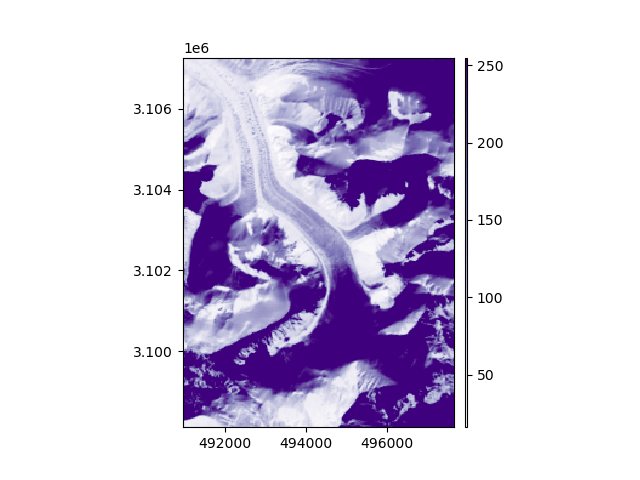
Second option: we can pass other crop_geom argument to crop(), including another Raster or a
simple tuple of bounds. For instance, we can re-crop the raster to be smaller than the vector.
rast.crop((rast.bounds.left + 1000, rast.bounds.bottom, rast.bounds.right, rast.bounds.top - 500), inplace=True)
rast.plot(ax="new", cmap="Purples")
vect.plot(ref_crs=rast, fc="none", ec="k", lw=2)
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.471 seconds)
