Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Polygonize a raster#
This example demonstrates the polygonizing of a raster using geoutils.Raster.polygonize() and geoutils.Mask.polygonize().
We open a raster.
import geoutils as gu
filename_rast = gu.examples.get_path("exploradores_aster_dem")
rast = gu.Raster(filename_rast)
rast.crop([rast.bounds.left, rast.bounds.bottom, rast.bounds.left + 5000, rast.bounds.bottom + 5000])
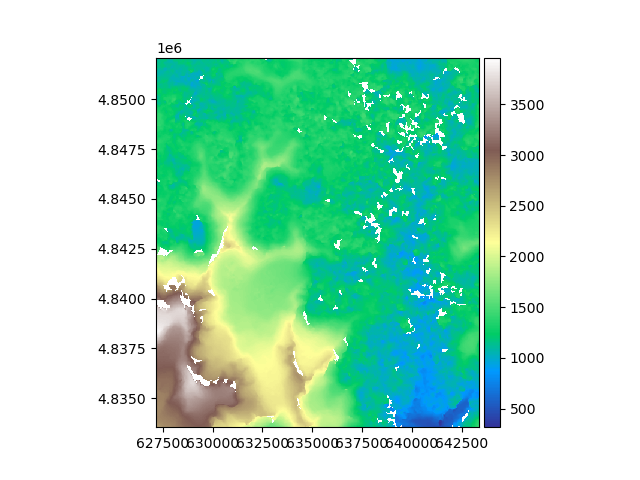
Let’s plot the raster.
rast.plot(cmap="terrain")
We polygonize the raster.
rast_polygonized = rast.polygonize()
rast_polygonized.plot(ax="new")
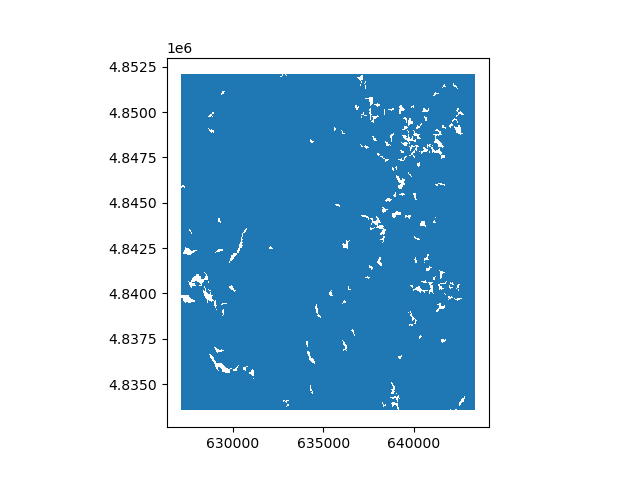
By default, polygonize() will try to polygonize target all valid values. Instead, one can specify discrete values to target by
passing a number or list, or a range of values by passing a tuple.
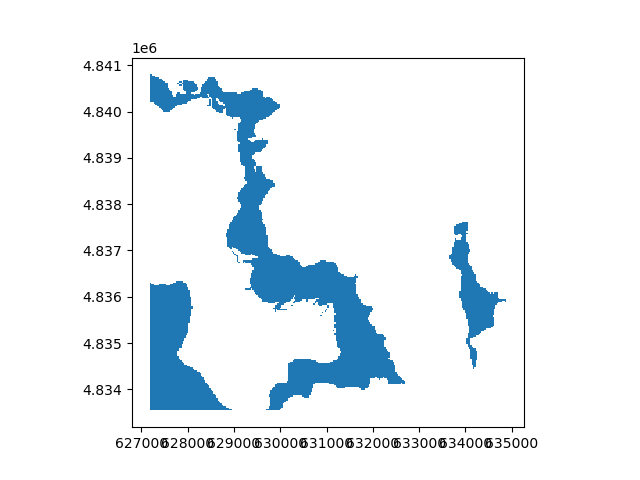
# A range of values to polygonize
rast_polygonized = rast.polygonize((2500, 3000))
rast_polygonized.plot(ax="new")
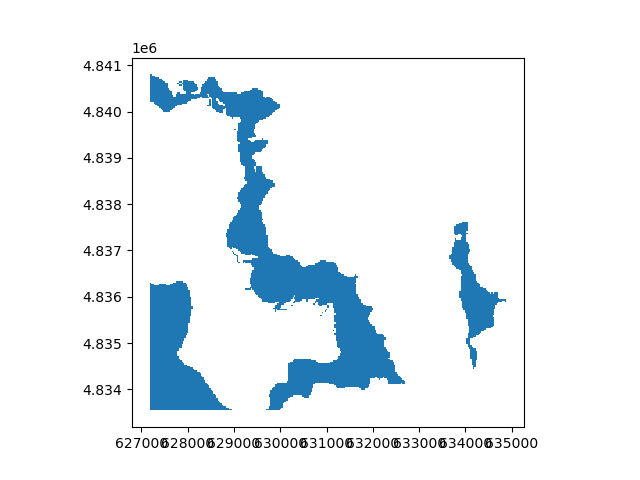
An even simpler way to do this is to compute a Mask() to polygonize using logical comparisons on the Raster().
rast_polygonized = ((2500 < rast) & (rast < 3000)).polygonize()
rast_polygonized.plot(ax="new")
Note
See Support of pythonic operators for more details on casting to Mask().
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 48.304 seconds)
